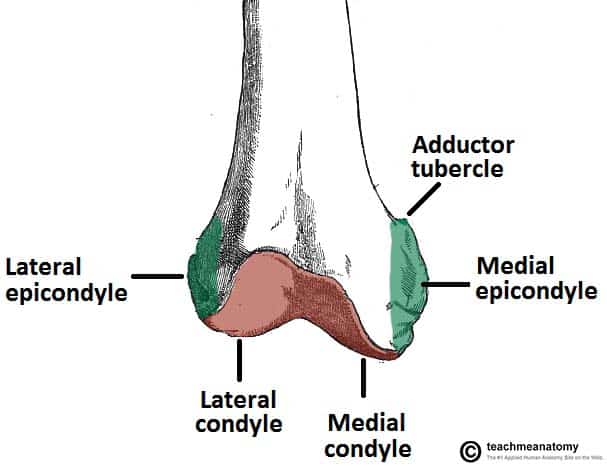
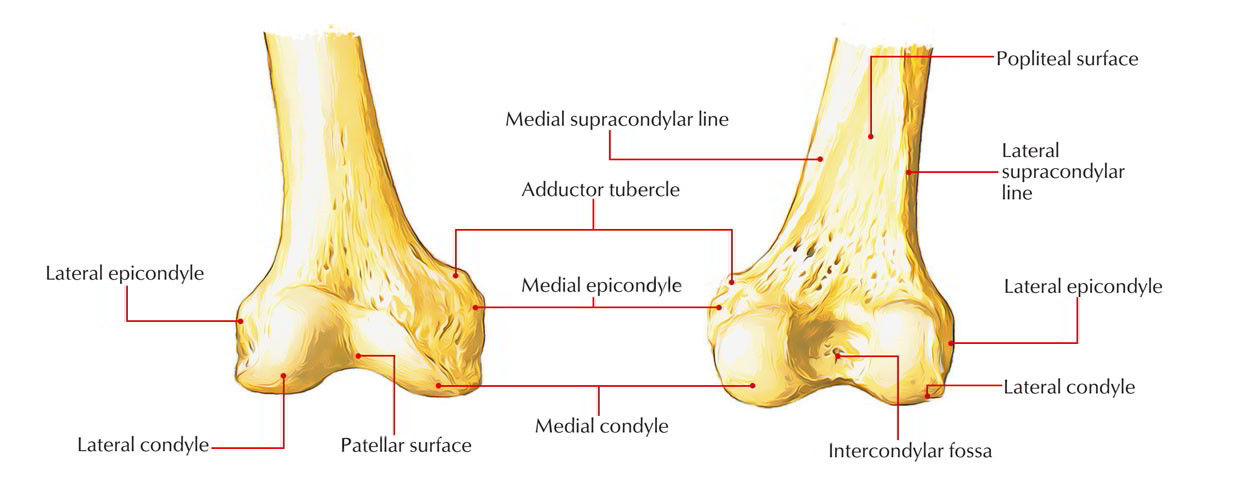
The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. Adductor tubercle Patella N507TG3-06TG3-56 N511.
Lateral femoral cutaneous n.
. Internally rotate the leg until the femoral epicondyles are positioned parallel with the IR. Located above the medial condyle it bears an elevation the adductor tubercle which serves for the attachment of the superficial part or tendinous insertion of the adductor magnus. Bones and area to remember.
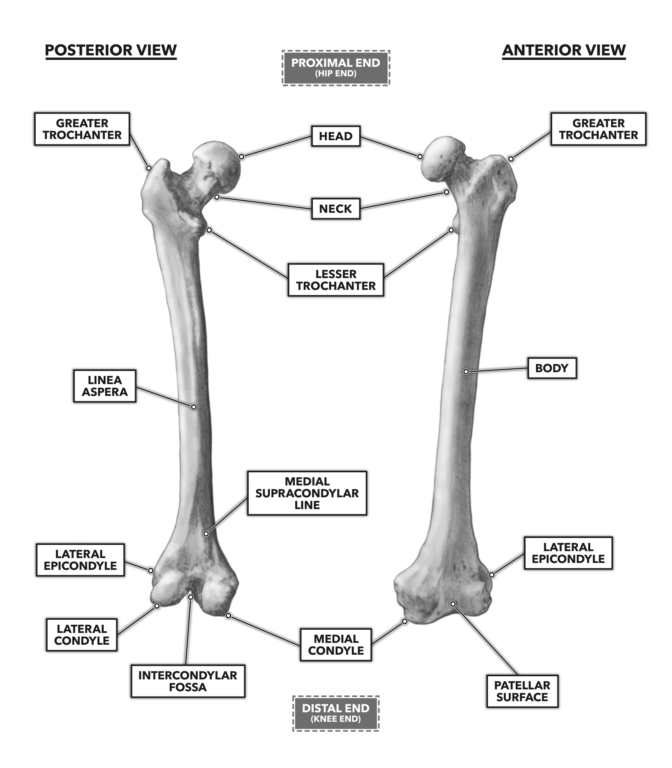
4 rows Distal end - lateral and medial condyles intercondylar fossa lateral and medial. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. Medial and lateral epicondyles bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles.
Crural fascia - leg fascia. The medial and lateral collateral ligaments of the knee originate from their respective epicondyles. They usually form part of a more complex fracture around the femoral component.
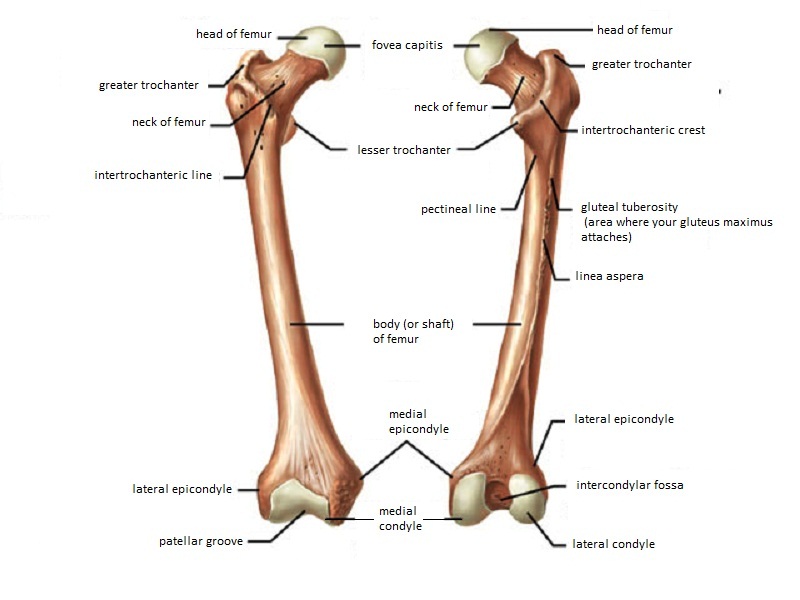
Know the Head of the Femur and that it attaches to the hip joint called the Acetabulum. The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle a bony protrusion located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end. The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia articulate with the a.
03 and good repeatability in vivo 02 RSMD. Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur d. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle.
Medial lateral epicondyles Pectineal line of femur. Located above the medial condyle it bears an elevation the adductor tubercle which serves for the attachment of the superficial part or tendinous insertion of the adductor magnus. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extr.
Head of the fibula e. The condylar axis determined by 3D ultrasound showed good accuracy in vitro 16 SD. The DynaKAD method applied to the walking calibration movement determined the medial-lateral axis closest to the ultrasound reference.
Medial condyle is much larger and bears more weight. The thigh bone is called the Femur. On the femur two types of condyles occur in the knee joint.
The medial epicondyle of the femur is a bony protrusion located on the medial side of the bones distal end. The Femur has a Greater Lessor Trochanter. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint.
Femur Pelvic Bone Connection. The medial epicondyle is the larger. Medial and lateral condyle.
The leg was externally rotated. The medial and lateral condyle of the tibia are shown in figure 1. In Condyle the medial condyle is larger in size and withstand more pressure while the lateral condyle is smaller in size but more prominent.
They are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa proximally bounded by the horizontal intercondylar line. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. The femoral epicondyles are not in profile the medial femoral condyle appears larger than the lateral condyle and the tibia superimposes more than one half of the fibular head.
Isolated medial or lateral epicondyle fractures are rare. The medial epicondyle of the femur is a bony protrusion located on the medial side of the bones distal end. On each condyle is a smaller epicondyle which serve as the point of attachment for the collateral ligaments the medial collateral MCL and the lateral collateral ligaments LCL.
It contains two facets for. N544 TG3-02 Femoral n. Greater and lesser trochanters of the femur.
N500 TG3-17 N540 TG3-63 Anterior femoral cutaneous nn. Medial and Lateral Epicondyles of Distal Femur a rough prominences for attachments of the medial and lateral collateral ligaments and are located on the outermost portions of the condyles. Tibial condyle Saphenous opening - for greater saphenous v.
There are two condyles found on the proximal end of the tibia and those are known as the medial and lateral condyles of tibia. Lateral Medial Epicondyles. In between the medial and lateral femoral condyles is the intercondylar fossa.
There are four main types of Epicondyle which are medial epicondyle of the humerus lateral epicondyle of the humerus medial epicondyle of the femur and lateral epicondyle of the femur. Subsequently one may also ask what ligament attaches to the. Which bone does not.
Intercondylar fossa a deep notch on the posterior surface of the femur between the two condyles. Learn more about the femur in this anatomy tutorial. Apex of the patella b.
Also is the lateral femoral condyle weight. It also contains both medial and lateral condyles. The medial and lateral condyles form the proximal part of the body of femur and articulate with the proximal part of tibia to form the femorotibial joint.
Lateral condyle is broader than medial condyle of the femur. Medial and lateral condyles of the femur c. The conventional method used markers over the femoral epicondyles.
Located above the medial condyle it bears an elevation the adductor tubercle which serves for the attachment of the superficial part or tendinous insertion of the adductor magnus. The medial condyle alongside the adductor tubercle is more prominent of the two. The medial and lateral condyles are found on the distal end of the femur and those articulate with the knee joint.
These fractures are classified by UCPF as V3-A. Tibia refers to the shin bone. This tendinous part here forms an intermuscular septum which forms.
Femur - largest long bone Medial lateral epicondyles Tibia Medial malleolus - medial ankle Fibula Lateral malleolus - lateral ankle Investing Fascia Fascia lata - envelopes thigh Iliotibial tract - lateral thickening attached to lat.
The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Femur Anatomy And Attachments Bone And Spine
What Is The Difference Between Condyle And Epicondyle Quora
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture


0 comments
Post a Comment